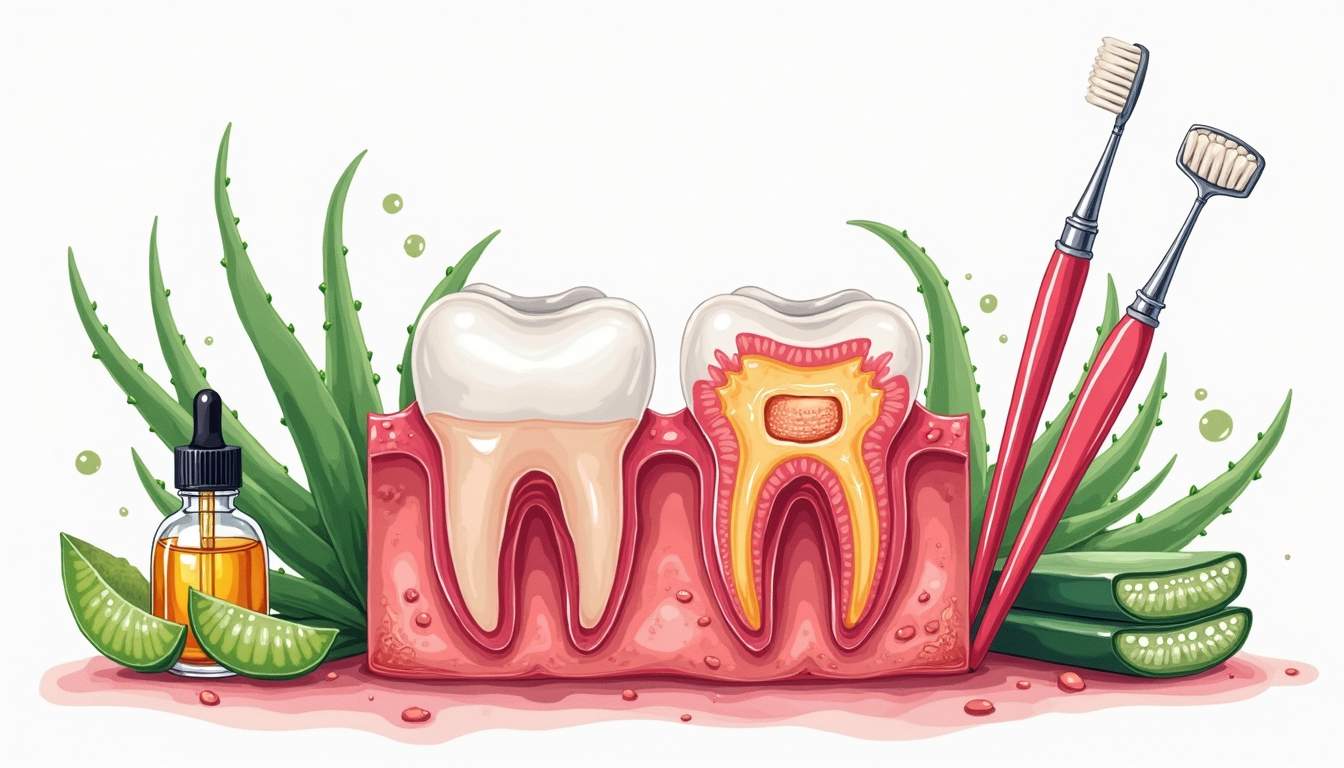
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet often overlooked condition that can have serious implications for oral health. Affecting millions of people worldwide, it begins with inflammation of the gums and can progress to tooth loss and other health issues if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments available is crucial for maintaining good oral hygiene and overall health.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease primarily arises from the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. When not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to more severe gum problems. The two main stages of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis: The Early Stage
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease and is characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, especially during brushing or flossing. At this stage, the condition is generally reversible with proper oral hygiene practices. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings play a vital role in preventing gingivitis from advancing.
Common causes of gingivitis include poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Awareness of these factors can help individuals take proactive measures to safeguard their gum health. For instance, pregnant women often experience hormonal changes that can increase their susceptibility to gingivitis, highlighting the importance of tailored dental care during different life stages. Additionally, individuals with conditions such as diabetes may have a higher risk of developing gum disease, making it crucial to manage these health issues effectively. To receive expert guidance and personalized care, consider a visit to Indental Castle Hill.
Periodontitis: A Serious Concern
If gingivitis is not addressed, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. This stage involves the destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. Symptoms may include persistent bad breath, receding gums, and loose teeth. Periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to other systemic health issues, such as heart disease and diabetes.
It is essential to recognize the signs of periodontitis early and seek professional treatment to prevent further complications. Regular dental visits can help monitor gum health and catch any issues before they escalate. Furthermore, treatment options for periodontitis may include deep cleaning procedures, scaling and root planing, and in some cases, surgical interventions to restore gum health. Patients are often encouraged to adopt a comprehensive oral care routine that includes the use of antimicrobial mouthwashes and possibly antibiotics to help control bacterial growth. Understanding the connection between oral health and overall well-being can empower individuals to prioritize their dental hygiene and seek timely care.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Being aware of the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and treatment. Many individuals may not realize they have gum disease until it has progressed significantly. Here are some common indicators:
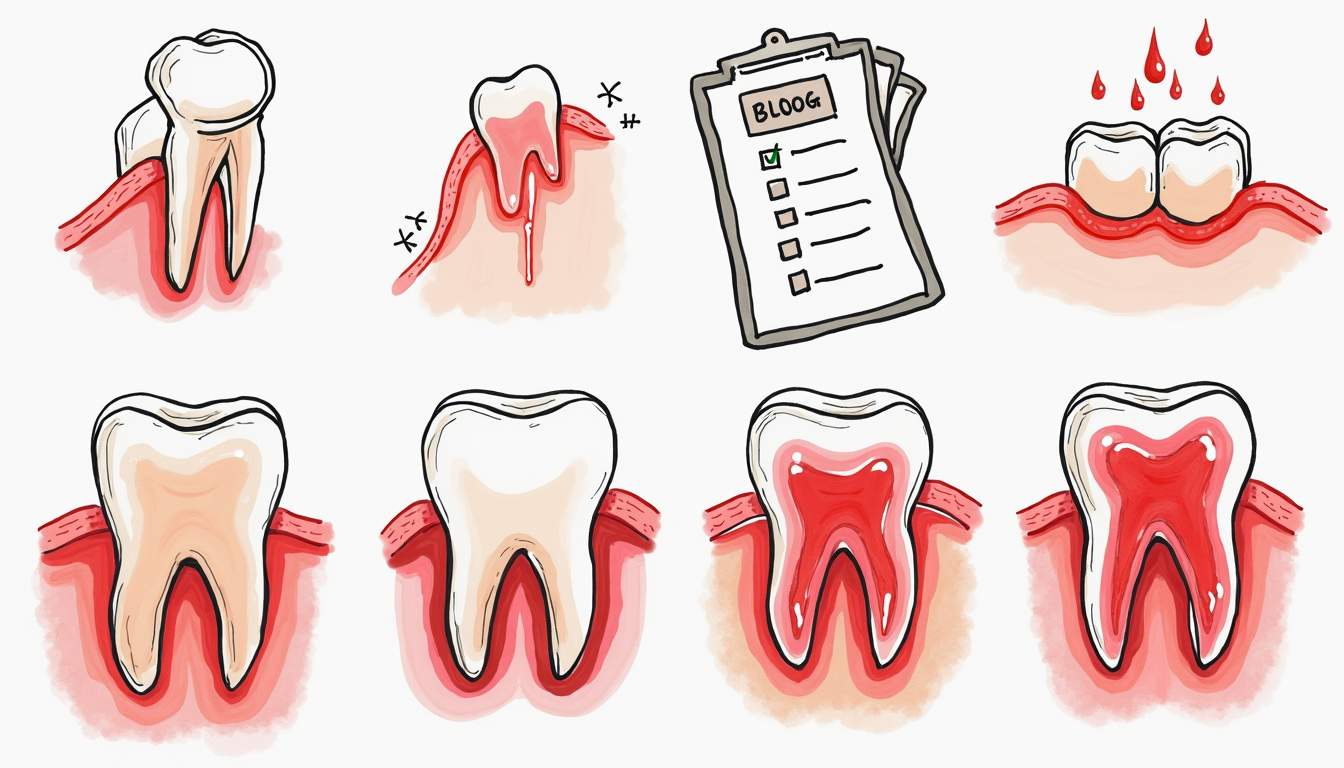
Common Symptoms
- Swollen or red gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
If any of these symptoms are present, it is vital to consult a dental professional for an evaluation. Early intervention can prevent the progression of gum disease and protect overall oral health. Ignoring these signs may lead to more severe complications, including tooth loss and infections that can affect other parts of the body.
In addition to the physical symptoms, individuals may also experience discomfort or pain in the gums, which can be a significant indicator of underlying issues. This discomfort can sometimes manifest as a dull ache or a sharp pain, especially when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods. Recognizing these sensations and addressing them promptly can be key to maintaining gum health.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gum disease. These include:
- Age: The risk increases with age, making regular dental check-ups even more critical.
- Smoking: Tobacco use significantly contributes to gum disease and hinders healing.
- Genetics: A family history of gum disease can predispose individuals to similar issues.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and autoimmune diseases can affect gum health.
Understanding these risk factors can empower individuals to take preventive measures and seek timely treatment. For instance, individuals with diabetes should be particularly vigilant about their oral hygiene, as the disease can impair blood flow and reduce the body’s ability to fight infections. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can also increase susceptibility to gum disease, making it essential for women to monitor their oral health closely during these times.
Moreover, poor nutrition can play a significant role in gum health. A diet lacking in essential vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, can weaken the gums and make them more prone to disease. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can not only enhance overall health but also fortify the gums against potential threats. Regular dental cleanings and good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, are also vital in combating these risk factors and maintaining healthy gums.
Preventing Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to gum disease. Adopting a proactive approach to oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum problems.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is essential. This includes brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily to remove plaque between teeth. Additionally, using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease.
Regular dental check-ups, typically every six months, are crucial for professional cleanings and early detection of any potential issues. Dentists can provide personalized advice based on individual needs and risk factors.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Incorporating healthy lifestyle choices can also contribute to gum health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, supports gum tissue health. Staying hydrated and avoiding sugary snacks can further reduce plaque buildup.
Moreover, quitting smoking can dramatically improve oral health. Not only does it reduce the risk of gum disease, but it also enhances overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
If gum disease is diagnosed, various treatment options are available depending on the severity of the condition. Early intervention can often lead to simpler and more effective treatments.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For mild cases of gingivitis, non-surgical treatments are typically sufficient. These may include:
- Professional Cleaning: A dental hygienist will perform a thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure involves scraping away plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smoothing the tooth roots to promote healing.
Following these treatments, patients are often advised to maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent recurrence.
Surgical Treatments
In more advanced cases of periodontitis, surgical interventions may be necessary. These treatments can include:
- Flap Surgery: The gums are lifted back to remove tartar deposits and then sutured back in place for better gum health.
- Bone Grafts: If bone loss has occurred, grafting can help regenerate lost bone and support the teeth.
- Tissue Grafts: This procedure involves taking gum tissue from another area of the mouth to cover exposed roots and promote gum growth.
These surgical options can be effective in restoring gum health, but they require a commitment to ongoing oral care to maintain results.
The Role of Technology in Gum Disease Treatment
Advancements in dental technology have revolutionized the way gum disease is diagnosed and treated. Modern techniques and tools enhance the effectiveness of treatments and improve patient comfort.
Laser Dentistry
Laser dentistry is becoming increasingly popular for treating gum disease. This minimally invasive technique uses focused light energy to remove infected tissue while preserving healthy gum tissue. The precision of lasers reduces bleeding and promotes faster healing.
Patients often report less discomfort and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgical methods, making laser treatment an appealing option for those with gum disease.
Digital Imaging
Digital imaging technology allows dentists to obtain detailed images of the teeth and gums, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. This technology helps identify areas of concern that may not be visible during a standard examination.
Furthermore, digital records enable better tracking of a patient’s oral health over time, making it easier to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Maintaining Gum Health After Treatment
After undergoing treatment for gum disease, maintaining gum health is essential to prevent recurrence. This involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices and regular dental visits.
Establishing a Routine
Creating a consistent oral care routine is vital. This includes brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash as recommended by a dental professional. Patients should also pay attention to their diet, ensuring it is rich in nutrients that support gum health.
Incorporating regular dental check-ups into one’s routine can help identify any potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Staying Informed
Staying informed about gum health and the latest advancements in dental care can empower individuals to make better choices for their oral health. Engaging with dental professionals and participating in educational programs can enhance understanding and awareness of gum disease.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a significant health concern that can lead to serious consequences if not addressed promptly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for maintaining oral health. By adopting preventive measures, seeking timely treatment, and staying informed, individuals can protect their gums and overall well-being.
Prioritizing oral health is not just about having a beautiful smile; it is about ensuring long-term health and quality of life. Regular dental visits, good oral hygiene practices, and a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in preventing gum disease and promoting a lifetime of healthy smiles.